Understanding Tarantula Hawks
The tarantula hawk, a formidable and striking insect, is a species of spider wasp. Known for their impressive size and unique behavior, these wasps have captivated the attention of entomologists and nature enthusiasts alike. Understanding these creatures, from their physical characteristics to their ecological role, is the first step in appreciating the importance of mapping their nesting sites and contributing to their conservation. Their life cycle, hunting habits, and preferred habitats provide a rich context for the process of mapping and studying these fascinating insects. Learning about them enhances our knowledge about the ecosystems they inhabit and the roles they play within their environment. The tarantula hawk is a symbol of both danger and beauty in the desert and arid regions where they are commonly found.
What is a Tarantula Hawk
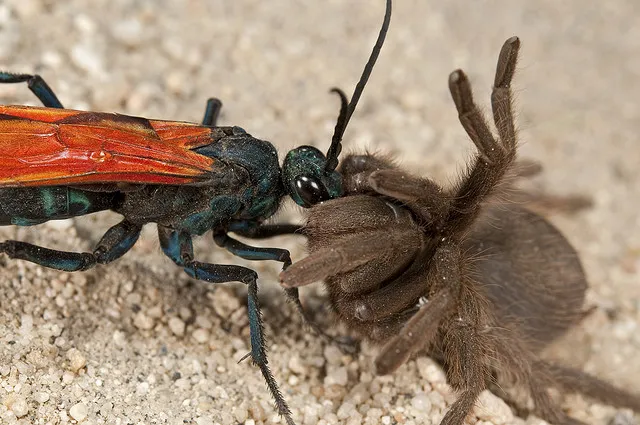
Tarantula hawks are large, powerful wasps belonging to the genus Pepsis and Hemipepsis. These wasps are renowned for their hunting behavior, specifically targeting tarantula spiders. Their sting is considered one of the most painful insect stings, though it is not typically dangerous to humans. The wasps’ striking appearance, with their iridescent blue-black bodies and orange or rusty wings, makes them easily recognizable. They are solitary insects, and the females are responsible for hunting and paralyzing tarantulas to serve as hosts for their larvae. They are native to the Americas, particularly in the southwestern United States and parts of South America, where they are important predators and play a vital role in controlling spider populations. Observing and studying the tarantula hawk is an amazing opportunity to know more about the balance of nature.
Tarantula Hawk Characteristics
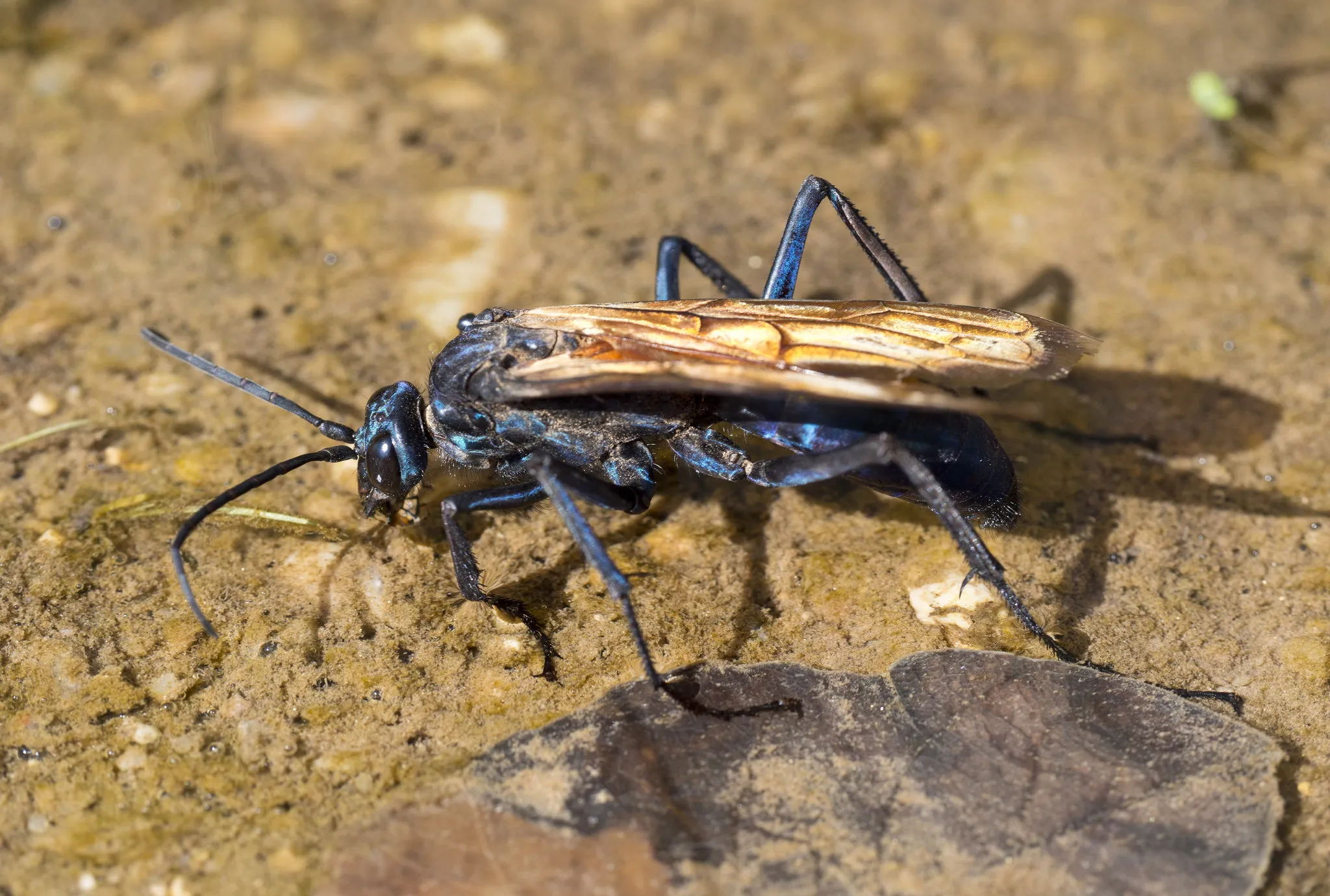

Tarantula hawks are among the largest wasps in the world, with females reaching up to 2 inches in length. Their bodies are robust and built for strength, allowing them to subdue large prey. The most distinctive feature is their coloration; the body is often a deep blue or black, contrasting with vibrant orange or rust-colored wings. The size and bright colors serve a dual purpose, warning potential predators and aiding in mate recognition. The wasps also possess a potent stinger, used to paralyze their prey. The life cycle begins when the female wasp hunts and stings a tarantula, paralyzing it. She then drags the spider to a burrow or nest and lays a single egg on the spider’s abdomen. The larva hatches and feeds on the paralyzed spider, eventually pupating and emerging as an adult wasp. Their remarkable life cycle and physical characteristics are some of the reasons why they are of interest to scientists.
Why Map Tarantula Hawks
Mapping tarantula hawk nests is crucial for several reasons, primarily related to conservation efforts and understanding the distribution and behavior of these wasps. By locating and monitoring nesting sites, researchers can gather valuable data about the species’ population dynamics, habitat preferences, and response to environmental changes. The information gathered helps inform conservation strategies and protect these fascinating insects and their habitats. Mapping nests allows for the assessment of environmental impacts, such as habitat loss or pesticide use, and their potential effect on tarantula hawk populations. With increasing human encroachment, mapping provides insights into how these wasps adapt and survive in a changing world. Mapping contributes to a better understanding of the broader ecosystem and the roles different species play, while ensuring their survival for future generations.
Benefits of Mapping Tarantula Hawk Nests
Mapping tarantula hawk nests provides many benefits, including insights into the species’ distribution, population size, and habitat preferences. This data aids conservation efforts by identifying critical habitats and areas where these wasps are most vulnerable. Monitoring nest locations allows for assessing environmental impacts, such as habitat loss or pesticide use. This is particularly important in areas where human activities overlap with tarantula hawk habitats. The maps also help in studying their behavior, like nesting habits and mate selection. Community mapping projects can engage the public in scientific research, raising awareness and fostering a sense of responsibility. The maps are invaluable resources for researchers, conservationists, and educators, facilitating a deeper understanding of this important species and the ecosystems they inhabit. They can also serve to inform land-use planning, helping to minimize disturbance to the wasps and their habitat.
Conservation Efforts and Tarantula Hawks

Mapping is directly linked to conservation efforts, as it provides essential data for protecting tarantula hawk populations. Understanding where these wasps nest allows for targeted conservation measures, such as habitat preservation, minimizing pesticide use, and promoting responsible land management practices. Conservationists use mapping data to identify and protect critical habitats, safeguarding the resources these wasps need to survive and reproduce. Public awareness campaigns can educate communities about the importance of tarantula hawks and the threats they face, encouraging support for conservation initiatives. By monitoring population trends and habitat changes, conservation efforts can be adapted to address emerging threats. As climate change alters habitats, mapping is critical for understanding how the tarantula hawks are responding. This information ensures that conservation strategies are effective and can evolve to meet the challenges.
How to Map Tarantula Hawk Nests
Mapping tarantula hawk nests requires a systematic approach, combining observation, data collection, and the use of appropriate tools and techniques. It begins with identifying potential nesting sites, often based on the wasps’ preferred habitats and behaviors. Gathering the necessary materials, such as GPS devices, notebooks, and cameras, ensures accurate data recording. Mapping techniques may include direct observation of nesting activity, marking nest locations with GPS coordinates, and documenting environmental factors. The process should always prioritize ethical considerations, minimizing disturbance to the wasps and their habitats. Careful documentation is essential for creating a comprehensive map. Sharing your map data with researchers and conservation organizations contributes to a broader understanding of the species and its conservation needs, making it essential to provide the best possible contribution.
Identifying Potential Nesting Sites
Identifying potential nesting sites is the first crucial step in mapping tarantula hawk nests. These wasps typically prefer areas with sandy or well-drained soil, where they can dig burrows or locate suitable pre-existing cavities. Look for these areas. The wasps also favor habitats with an abundance of tarantulas, as these spiders are their primary prey. The nesting sites are often in sunny locations. Observing the landscape can help in locating areas with these features. Time of day is critical. The wasps are most active during the warmer months, so conducting surveys during this period increases the chances of finding nests. Field guides and online resources can also provide valuable information about the wasps’ habitat preferences and nesting habits. Careful observations and detailed habitat assessments are the foundations for mapping success.
Gathering Necessary Materials

Gathering the right materials ensures that the mapping process is efficient and accurate. You will need a GPS device or a smartphone with GPS capabilities to record the exact locations of nests. A notebook and pen are essential for recording detailed observations, including the surrounding environment, nest characteristics, and any wasp activity. A camera is a valuable tool to document nest entrances, habitat details, and, if possible, the wasps themselves. Appropriate field equipment, like sturdy shoes, long sleeves, and insect repellent, is essential. Having safety items, like a first-aid kit and water, is also critical. By gathering all the necessary tools and supplies, you can ensure that your mapping efforts are successful and contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of tarantula hawk distribution and nesting behavior.
Mapping Techniques and Tools
Various mapping techniques can be used to effectively locate and document tarantula hawk nests. One common method involves direct observation, where you systematically search for nesting activity during peak activity periods. Use GPS devices or smartphone applications to record the exact locations of the nests. Detailed documentation is essential. Note the characteristics of the nest entrance, the surrounding vegetation, and any signs of wasp activity. Using a camera to take photographs provides valuable visual records. For larger-scale projects, consider using GIS (Geographic Information System) software. Using these tools, you can create detailed maps that show the distribution of nests. Combining different techniques ensures a comprehensive understanding of the wasps’ nesting patterns and habitat preferences. This process provides valuable data for conservation efforts.
Documenting Nest Locations
Accurately documenting nest locations involves more than just recording GPS coordinates. For each nest, you must meticulously record several pieces of information, providing context and aiding in analysis. Take notes on the exact GPS coordinates. Describe the nest entrance, including its size, shape, and any distinguishing features. Note the surrounding habitat, including the type of vegetation, soil composition, and any nearby landmarks. Document any wasp activity, such as the presence of adults, the dragging of a tarantula, or any other notable behaviors. Record environmental conditions, such as the time of day, temperature, and weather conditions. By providing detailed documentation, you create a comprehensive record. These detailed records are invaluable for understanding the factors influencing nest site selection, wasp behavior, and population dynamics. This allows for creating an accurate nest map.
Creating Your Tarantula Hawk Map

Once you’ve gathered all of the nest data, the next step is creating your tarantula hawk map. Creating a map involves choosing the right software, inputting your collected data, adding annotations, and sharing the findings. The map serves as a visual representation of the wasp’s distribution, habitat preferences, and other critical information. These maps are valuable for conservation efforts and for informing future research. The steps include choosing the right software, inputting the data and relevant annotations, and sharing your results. With that information, you are contributing to protecting tarantula hawks and their habitat.
Choosing Your Mapping Software
The choice of mapping software depends on the complexity of your project and your technical expertise. For basic mapping, many free and user-friendly options are available. Google My Maps is a simple tool that allows you to create custom maps by importing data and adding markers. For more advanced analysis and features, consider using GIS software like QGIS, which is open-source and offers a wide range of functionalities. Commercial options, such as ArcGIS, provide powerful tools for spatial analysis and data management. The choice depends on your project’s needs and your level of technical expertise. The important factor is that the software can handle the data you’ve collected, visualize the nest locations, and allow you to add annotations. Using the right software guarantees that you can present the data in a clear and informative way.
Inputting Data and Annotations
Inputting your collected data into the mapping software is a crucial step in creating a useful and informative map. Begin by entering the GPS coordinates of each nest into the software. Then, add the descriptive information you documented for each nest. Include the habitat, nest entrance characteristics, and any observations of wasp activity. Annotate the map with relevant information. You can add labels, notes, and symbols to represent different nest characteristics or environmental factors. You can also add layers to show additional details, such as elevation, land cover, or protected areas. This helps in giving the map a comprehensive context. Using the annotation tools, you can create a clear and informative visual representation of your data.
Sharing Your Map and Findings

Sharing your map and findings is essential for contributing to scientific knowledge and conservation efforts. Make your map accessible to others. You can share it with researchers, conservation organizations, and the public. Consider publishing your findings in scientific journals or presenting them at conferences. Providing a copy of your map with detailed documentation allows others to understand the methods and results. Sharing your map on online platforms, such as research repositories or community mapping sites, increases its visibility. You can also create a website or blog to showcase your work and engage with others interested in tarantula hawk conservation. The collaboration is important. This enables you to contribute to a broader understanding and protection of these wasps.
Ethical Considerations for Mapping Tarantula Hawks
Mapping tarantula hawk nests should always be conducted with careful attention to ethical considerations, prioritizing the welfare of the wasps and their habitats. Minimize disturbances to their natural environment and behavior. Always obtain necessary permits before conducting any research activities. Respect the privacy of the wasps. Ensure that your actions do not cause harm or stress. If you are working on private land, obtain permission from the landowner. Avoid handling or approaching the wasps, as they can sting and cause pain. Never remove or disturb any nests. Adhering to these ethical principles is essential for responsible mapping, ensuring that your efforts contribute to the conservation of these remarkable creatures.
Minimizing Disturbances
Minimizing disturbances is critical to the ethical conduct of mapping tarantula hawk nests. Stay a safe distance from the nests and avoid any actions that might disrupt the wasps’ behavior. Do not make loud noises, move around frequently, or make any sudden movements, as these can scare or agitate them. Avoid altering the habitat around the nests. Refrain from disturbing the soil or vegetation and never attempt to handle or capture the wasps. When conducting surveys, use techniques that minimize the impact on the environment. When using GPS devices or cameras, do not leave any equipment behind. By reducing the impact on the wasps, you ensure that your mapping efforts do not harm their survival and reproduction. Respect their place in nature and make sure the observations remain a positive contribution.
Respecting Wildlife Habitats

Respecting wildlife habitats is fundamental to responsible mapping. Stay within the designated trails and avoid trampling vegetation or disturbing the natural environment. Do not remove any plants or animals from the area, as this can disrupt the ecosystem. Be mindful of your impact on the soil, avoid compacting it. Be careful when handling equipment. Use biodegradable materials and remove all trash. Respect the natural processes that shape the habitat. Do not interfere with the natural flow of water or the movement of animals. This respect for the environment will have positive effects. The conservation of these species is crucial for maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems and is beneficial for future generations.
Tarantula Hawk Nest Map Examples
Studying existing tarantula hawk nest maps can provide inspiration and demonstrate effective mapping techniques. The maps usually show nest locations, habitat characteristics, and relevant environmental data. You can learn how to present your findings in a clear and informative way by studying other examples. You can understand different approaches by studying them and adapting these methods to your own project. Look for maps created by researchers, conservation organizations, or citizen science initiatives. These maps often include detailed information, such as the date of data collection, the mapping methods used, and the geographic scale. They also highlight the importance of data visualization. Learning from these examples will give you the tools you need to create a comprehensive and effective map.
Where to Find Examples
Several resources can help you find examples of tarantula hawk nest maps. Scientific journals and research papers often include maps as part of their studies on insect distribution and behavior. Search online databases. Websites of conservation organizations and government agencies may also have maps or datasets related to tarantula hawks and their habitats. Explore citizen science projects. These often involve community mapping efforts. Look for projects on platforms like iNaturalist, where users share observations of wildlife. Using these resources, you can find a wide range of examples, learn how to create your own maps, and contribute to the mapping community.
Interpreting Map Data

Interpreting map data is essential for extracting meaningful insights. Study the distribution of nests across different geographic areas. Look for patterns and clusters. Examine the relationship between nest locations and environmental factors, such as soil type, vegetation, and climate. Identify any correlations between nest density and human activities, such as land use or pesticide use. Analyze how the wasp’s behavior, nesting habits, and habitat preferences. Compare the map data with existing ecological data, such as habitat maps or climate data. Analyze the map to understand the factors that influence the wasps’ distribution and the threats they face. This understanding is important for developing effective conservation strategies.
Future of Tarantula Hawk Mapping
The future of tarantula hawk mapping involves exciting possibilities, with emerging advancements in technology. These advancements will significantly improve the accuracy, efficiency, and scope of mapping efforts. The goal is to enhance data collection, analysis, and dissemination. It will contribute to conservation efforts. New opportunities will make mapping activities easier and more effective. Through innovation and collaboration, the future of tarantula hawk mapping is promising.
Advancements in Mapping Technology
Advancements in mapping technology offer the opportunity to improve the way we map tarantula hawks. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras can be used for aerial surveys, providing detailed images of nesting sites and surrounding habitats. Mobile apps with integrated GPS and data-logging features. These make it easier to collect and record nest locations. Machine learning algorithms can analyze large datasets, automating the process of identifying potential nest locations. Using satellite imagery and remote sensing techniques, the researchers can assess habitat conditions and monitor changes over time. These technological advances promise to revolutionize the field of tarantula hawk mapping. This will enable researchers to collect more data, analyze it and create a more comprehensive understanding of the species.
Collaborative Mapping Projects
Collaborative mapping projects engage communities. Citizen science initiatives involve volunteers in data collection and analysis. These projects are essential for mapping tarantula hawks. These collaborative approaches increase the geographic scope and scale of mapping efforts, expanding our understanding. This contributes to raising public awareness. These projects also empower communities. They also encourage a sense of responsibility for the conservation of these wasps. Open data platforms and online communities enable the sharing of information and the collaboration of researchers and volunteers. Such collaborations are the future of tarantula hawk mapping. This is an essential way to protect and learn about these insects.
In conclusion, mapping tarantula hawk nests is a valuable endeavor that contributes to our knowledge of these wasps and their conservation. This includes understanding tarantula hawks, why mapping is important, and how to create a map, the ethical considerations, and some examples. By engaging in mapping efforts, we are contributing to a broader understanding of the ecosystems and the roles that different species play. Remember, our shared responsibility is to protect these fascinating insects.