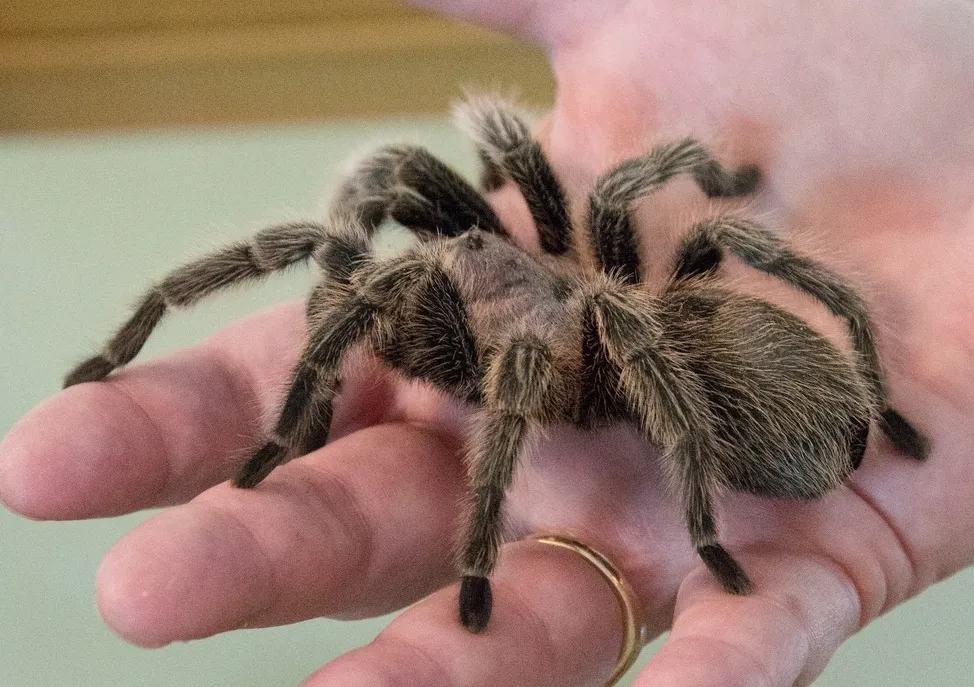
Tarantula Testing Online 7 Astonishing Facts
Embark on an extraordinary journey into the captivating world of tarantulas. These fascinating creatures, often misunderstood, are actually quite remarkable, exhibiting a complex array of behaviors and adaptations. This article aims to unveil seven astonishing facts about tarantulas, shedding light on their unique characteristics and dispelling common misconceptions. By exploring these facts, you’ll gain a newfound appreciation for these often-feared but undeniably intriguing animals. Whether you’re a seasoned arachnid enthusiast or simply curious, prepare to be amazed by the wonders of the tarantula.
What are Tarantulas
Tarantulas, belonging to the Theraphosidae family, are large and hairy spiders that are found in various habitats across the globe. They are characterized by their imposing size, with some species boasting leg spans exceeding 10 inches. Unlike many other spiders, tarantulas possess urticating hairs on their abdomens, which they can flick at predators as a defense mechanism. These spiders are nocturnal hunters, primarily feeding on insects, but larger species may also consume small vertebrates like lizards and rodents. Their longevity is also quite remarkable, with some females living for over 20 years. Understanding the basic characteristics of tarantulas is crucial for appreciating the astonishing facts that follow.
The Origins and Habitat of Tarantulas
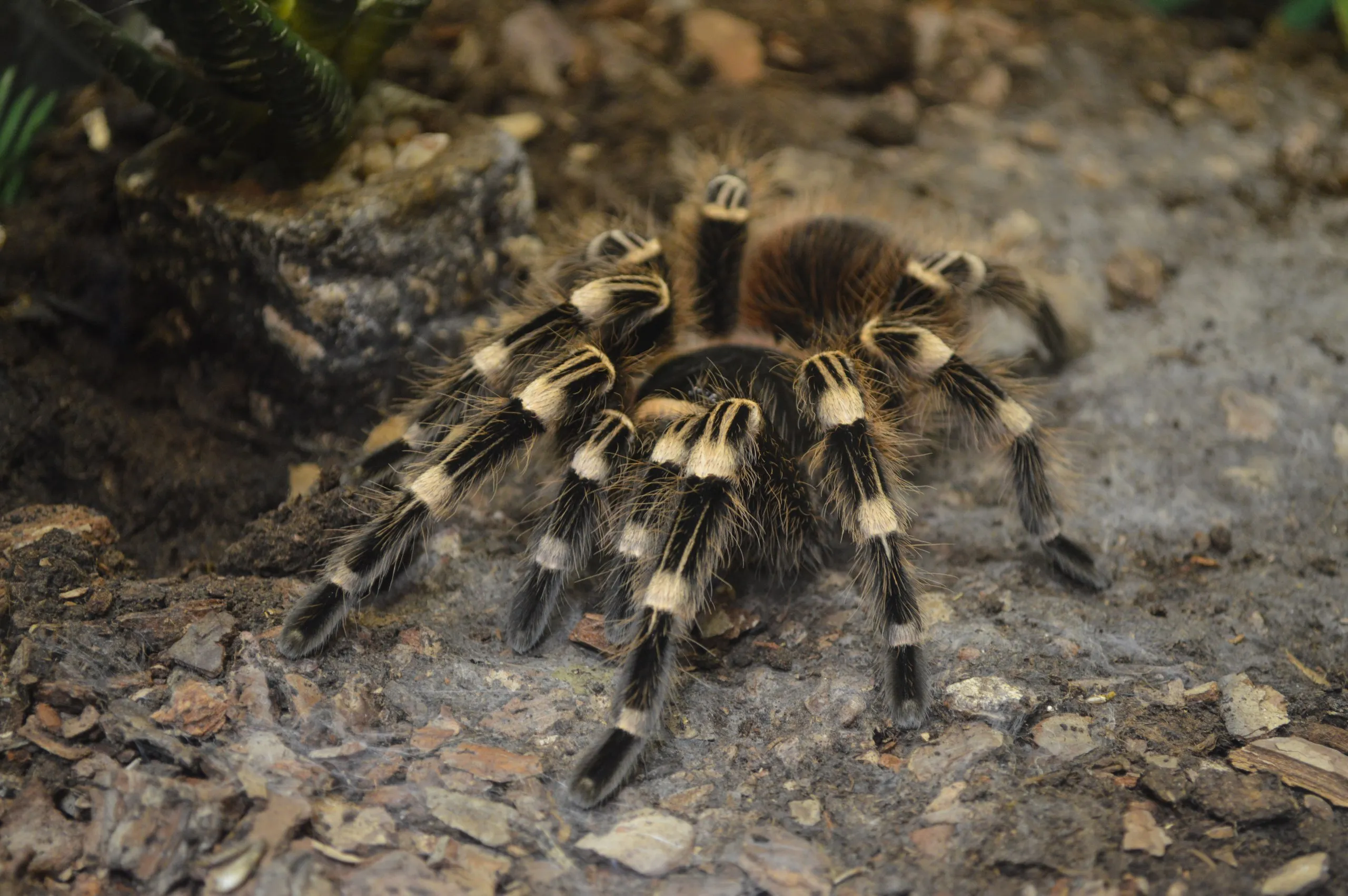

Tarantulas have a rich evolutionary history, with fossils suggesting their existence dates back millions of years. They are believed to have originated in the Americas and have since spread to various regions. Today, tarantulas inhabit diverse environments, from the tropical rainforests of South America to the arid deserts of North America and the grasslands of Africa and Asia. Their habitats play a significant role in shaping their adaptations, with some species burrowing underground, while others construct webs in trees or under rocks. The distribution and adaptability of tarantulas highlight their resilience and success as a species, thriving in a multitude of ecological niches. Understanding their origins and habitats adds context to their fascinating lives.
Characteristics of Tarantulas
Tarantulas possess a range of characteristics that distinguish them from other spider species. Their physical attributes, including their size, coloration, and the presence of urticating hairs, are key identifiers. Behaviorally, tarantulas exhibit complex hunting strategies, mating rituals, and defensive mechanisms. They are typically solitary creatures, except during mating season or when females are guarding their eggs. The study of tarantula characteristics provides valuable insights into their ecological roles and evolutionary adaptations. This includes understanding their sensory abilities and how they interact with their environment. These elements come together to create a unique creature that has captivated scientists and enthusiasts alike.
Physical Attributes
Tarantulas are easily recognized by their large size and hairy bodies. The size varies greatly depending on the species, with some reaching leg spans of over 10 inches. Their bodies are divided into two main parts: the cephalothorax (head and thorax fused) and the abdomen. They have eight legs, two pedipalps (used for sensing and manipulating prey), and eight eyes. The coloration of tarantulas varies widely, ranging from black and brown to vibrant blues, oranges, and reds, often serving as camouflage within their habitats. The presence of urticating hairs on their abdomen is a key defense mechanism, causing irritation to potential threats.
Behavioral Traits

Tarantulas exhibit diverse behavioral traits that are fascinating to observe. They are primarily nocturnal hunters, using their sensory abilities to detect prey. Their hunting strategies vary, from ambush predators to active stalkers. Mating rituals involve complex displays and courtship behaviors, with the male carefully approaching the female to avoid being mistaken for prey. Defensive behaviors include raising their front legs, flicking urticating hairs, and biting. The solitary nature of most tarantulas, except during mating or when guarding eggs, also contributes to their unique behavioral patterns. The behavioral traits of tarantulas are critical to their survival.
7 Astonishing Facts About Tarantulas
Fact 1 Unique Silk Production
Tarantulas produce silk, though not to the extent of web-spinning spiders. They use silk to create retreats, line burrows, and wrap their prey. The silk of tarantulas is incredibly strong and versatile, with some species even using it to create trip lines. Unlike many web-spinning spiders, tarantulas do not rely on silk for catching prey; instead, they use it primarily for shelter and protection. The silk production is a remarkable feat of biological engineering, showcasing the adaptability of these creatures to various environments.
Fact 2 Venom Strength Variations
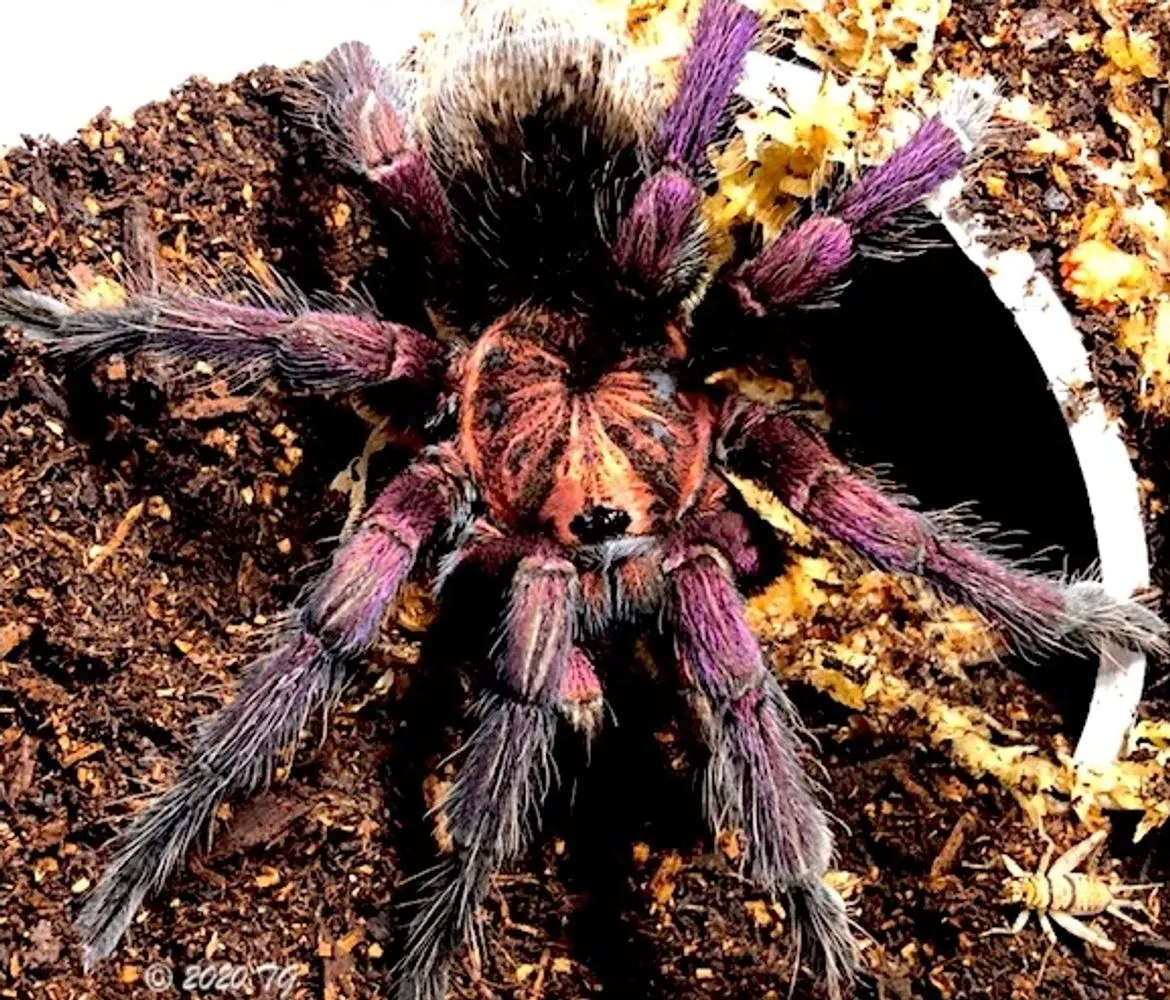

The venom of tarantulas varies greatly depending on the species. While all tarantulas possess venom, the potency and effects on humans differ significantly. Some species have relatively mild venom, causing localized pain and discomfort, while others may cause more severe symptoms. The venom is primarily used to subdue prey, injecting paralyzing agents. Contrary to popular belief, tarantula bites are rarely life-threatening to humans, but can still be quite unpleasant. The study of tarantula venom also contributes to the field of medical research, helping to understand the complex biochemical processes involved.
Fact 3 Molting Process
Tarantulas, like all arthropods, undergo a process called molting, where they shed their exoskeletons to grow. This process is essential for their development, as the exoskeleton cannot grow. Molting is a vulnerable time for tarantulas, as they are soft-bodied and defenseless. The frequency of molting decreases as they mature, with young tarantulas molting several times a year and adults molting less frequently. Before molting, tarantulas often lose their appetite and become less active. After molting, the tarantula is larger and its colors may appear brighter. Molting is a remarkable survival mechanism that enables tarantulas to grow and thrive.
Fact 4 Lifespan Differences
Tarantulas have remarkably long lifespans compared to other spiders. The lifespan varies greatly between species and sexes. Male tarantulas typically live for a few years, while females can live for over 20 years. This longevity is due to a combination of factors, including a slow metabolism and the absence of major predators in their natural habitats. The long lifespans of female tarantulas allow them to reproduce multiple times, contributing to the stability of their populations. The lifespans also make them popular pets, as they can be companions for a long time.
Fact 5 Feeding Habits

Tarantulas are primarily carnivores, with their diet consisting mainly of insects. They are opportunistic hunters, feeding on whatever prey they can catch. Larger species may also consume small vertebrates, such as lizards and rodents. Tarantulas use their fangs to inject venom into their prey, paralyzing them before consuming them. The feeding habits of tarantulas play a vital role in controlling insect populations within their ecosystems. Tarantulas can go for long periods without eating, especially when molting or preparing for it. The feeding habits make them efficient predators.
Fact 6 Sensory Abilities
Tarantulas possess a range of sensory abilities that help them navigate their environment, hunt prey, and avoid predators. They have eight eyes, but their vision is not particularly sharp. They rely more on their sense of touch, using hairs on their legs and bodies to detect vibrations and air currents. They also have chemoreceptors that allow them to sense chemicals in the air, aiding in prey detection. These sensory abilities work together to provide them with critical information about their surroundings. The sensory abilities ensure their survival and success in various environments.
Fact 7 Popularity in the Pet Trade
Tarantulas have become increasingly popular pets in recent years. Their relatively low maintenance requirements, unique appearance, and docile nature make them appealing to many pet owners. The pet trade has contributed to the conservation efforts of some species, with breeders helping to reduce the pressure on wild populations. However, it’s crucial to research any pet before bringing them home. Responsible pet ownership involves providing a suitable habitat, proper care, and a thorough understanding of the animal’s needs. The popularity of tarantulas as pets has led to an increased demand for information on their care.
How to Care for a Tarantula
Creating the Ideal Tarantula Habitat
Creating a suitable habitat is essential for the health and well-being of a pet tarantula. The enclosure should be appropriately sized, with enough space for the tarantula to move around and create a burrow or hiding place. The substrate should be appropriate for the species, typically consisting of a mix of coco coir, peat moss, and vermiculite. The habitat needs to maintain the correct temperature and humidity levels, using a heat lamp and a hygrometer. Providing hiding places like cork bark or artificial plants is crucial for the tarantula’s security and comfort. Ensuring a safe and stimulating environment is paramount.
Feeding and Hydration
Feeding tarantulas is relatively straightforward. They should be fed live insects, such as crickets, mealworms, or roaches. The size of the prey should be appropriate for the tarantula’s size. Water should always be available, typically in a shallow dish. It’s essential to remove any uneaten food to prevent the growth of mold or mites. The feeding frequency depends on the species and age of the tarantula, with juveniles needing to be fed more frequently. The correct feeding practices will allow the tarantula to stay in shape.
Handling and Safety
While some tarantulas are docile and can be handled, it’s essential to exercise caution. Handling should be done carefully and only when necessary. Tarantulas can be easily injured if dropped. It is important to be very careful when doing so. It is also important to wash your hands after handling. Always know the tarantula’s behaviors and possible risks. Always supervise children when handling or observing tarantulas to prevent accidents.
Common Health Issues and Prevention
Tarantulas can be susceptible to various health issues, including mites, fungal infections, and dehydration. Regular monitoring of the enclosure and the tarantula’s behavior is crucial for early detection of problems. Maintaining a clean and properly humidified habitat can help prevent many health issues. Quarantine new tarantulas before introducing them to existing ones. Consulting with a veterinarian specializing in exotic animals is recommended if any health issues arise. Prevention is always the best way to avoid health problems.
