Tevo Tarantula Z Axis Mount Problems [Overview]
The Tevo Tarantula is a popular 3D printer known for its affordability and ease of modification. However, like any 3D printer, it can encounter issues. One of the most critical aspects of the Tevo Tarantula is its Z-axis mount, which controls the vertical movement of the print head. Problems with the Z-axis can lead to print failures, layer shifting, and other frustrating issues. This guide will explore the top 5 common problems associated with the Tevo Tarantula Z-axis mount and offer solutions to keep your printer running smoothly and producing high-quality prints. Understanding these problems will allow you to quickly diagnose and resolve issues, minimizing downtime and maximizing your 3D printing experience. A properly functioning Z-axis is essential for accurate and reliable 3D printing. By addressing these potential problems, you can ensure your Tevo Tarantula consistently delivers excellent results. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for troubleshooting and maintaining the critical Z-axis components of your 3D printer. The aim is to help you quickly identify and resolve any Z-axis related issues, thus improving the quality and reliability of your prints.
Z Axis Binding
Z-axis binding is a common issue where the Z-axis fails to move smoothly, resulting in inconsistent layer heights and print failures. This friction can cause the Z-axis to stick, skip steps, or produce a rough surface finish. Binding can be caused by several factors, and identifying the root cause is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Proper lubrication and alignment are essential to prevent this issue and ensure the smooth operation of your 3D printer. Recognizing the signs of Z-axis binding is the first step in resolving the problem and improving your print quality. The impact of Z-axis binding can range from minor imperfections to complete print failures, highlighting the importance of addressing this issue promptly. By understanding the causes and solutions, you can maintain the smooth and precise vertical movement of your print head, leading to more accurate and reliable prints.
Causes of Z Axis Binding

Several factors can contribute to Z-axis binding. One of the most common is insufficient lubrication of the Z-axis rods. Without proper lubrication, the rods can generate friction as the Z-axis moves up and down. Another cause is misalignment of the Z-axis rods. Even slight misalignments can cause the Z-axis to bind, especially during faster movements or when the print head is carrying a heavy load. Also, the lead screws or threaded rods used for the Z-axis can get bent or damaged, leading to binding. Dust and debris accumulation on the rods can also exacerbate the issue. Finally, the linear bearings, which facilitate the smooth movement of the Z-axis, can wear out or become damaged. Regular maintenance and inspection are key to identifying and preventing these causes of Z-axis binding, ensuring smooth and reliable 3D printing performance. The interaction of all these components must be considered to solve the problem of binding.
Solutions for Z Axis Binding
To resolve Z-axis binding, start by thoroughly lubricating the Z-axis rods with a suitable lubricant like lithium grease or PTFE-based lubricants. Wipe the rods clean of any old grease and apply a thin, even layer of the new lubricant. Next, ensure the Z-axis rods are perfectly aligned. Loosen any mounting hardware and carefully adjust the rods until they move freely without binding. Check the lead screws or threaded rods for any bends or damage and replace them if necessary. Clean the Z-axis rods regularly to remove any dust or debris that could cause friction. Inspect the linear bearings for wear and replace them if they are damaged. Regularly performing these maintenance steps will help prevent Z-axis binding and ensure the smooth operation of your 3D printer. Another suggestion is slowing down the Z-axis movement speed in your slicing software to reduce friction.
Misaligned Z Axis Rods
Misaligned Z-axis rods are a common issue that can significantly impact print quality. When the rods are not perfectly parallel, the print head may experience friction and binding, leading to inconsistent layer heights, layer shifting, and other print defects. Accurate Z-axis movement is crucial for achieving precise and reliable 3D prints. Misalignment often goes unnoticed initially, but its effects become more apparent as prints get taller and more complex. Regular checks and adjustments of the Z-axis rods are essential to maintaining optimal print performance. Identifying and correcting any misalignment can greatly improve the overall quality and consistency of your 3D prints, reducing the occurrence of failures. The alignment of the Z-axis rods is directly related to the precision of the vertical movements, which are vital for the accuracy of the printed object.
Identifying Misalignment
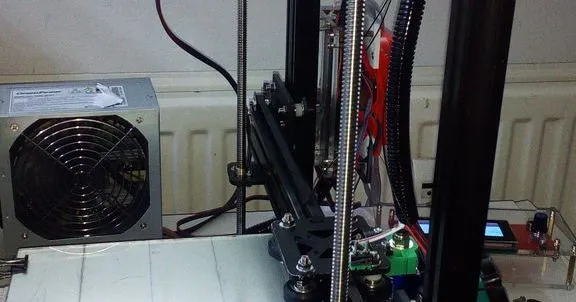
Identifying misalignment can be done through visual inspection. Look for any deviation in the vertical position of the Z-axis rods relative to each other. If one rod appears to be tilted or angled, misalignment is likely. Also, you can manually move the Z-axis up and down and feel for any resistance or binding. If the Z-axis does not move smoothly, misalignment is a possibility. Print a tall, single-walled object and observe if the layers are consistent. Inconsistent layer heights or any noticeable layer shifting can indicate misalignment. Use a level or a caliper to measure the distance between the Z-axis rods at different points. Any variations in these measurements indicate misalignment. These visual and tactile methods can help in identifying issues before they cause major printing failures. Proper alignment can significantly improve print quality.
Correcting Z Axis Rods Misalignment
To correct misalignment, first, loosen the screws or bolts that hold the Z-axis rods in place. This will allow you to adjust their positions. Ensure that the frame is square. Use a level or a ruler to ensure that the rods are perfectly parallel. Carefully reposition the rods until they are aligned. Once you achieve the correct alignment, gently tighten the screws or bolts while ensuring the rods remain in place. After tightening the screws, re-test the Z-axis movement to make sure it is smooth and without binding. If the rods are still misaligned, loosen the screws and repeat the process. Often, the frame itself is not perfectly square. In this case, adjusting the rod’s position may not be enough, and frame adjustments will be necessary. Regular checks and adjustments of the Z-axis rods are vital to maintaining optimal print performance and should be a part of your regular printer maintenance routine. This will minimize the potential for future misalignments and printing errors.
Loose Couplers
Loose couplers are another potential problem with the Tevo Tarantula Z-axis mount. The couplers connect the stepper motor to the Z-axis lead screws, which drive the vertical movement. If these couplers are not securely tightened, they can slip, leading to inconsistent layer heights and print inaccuracies. This is one of the simpler issues to resolve, but it can have a considerable impact on print quality. Ensuring that the couplers are tight and properly aligned is a simple yet effective way to prevent Z-axis related issues. This is often overlooked, but it’s a vital step. Regularly checking and tightening the couplers is a preventative measure that can save time and materials. The couplers are a direct link between the motor and the rods, so the tighter they are, the more accurate the results will be.
Symptoms of Loose Couplers
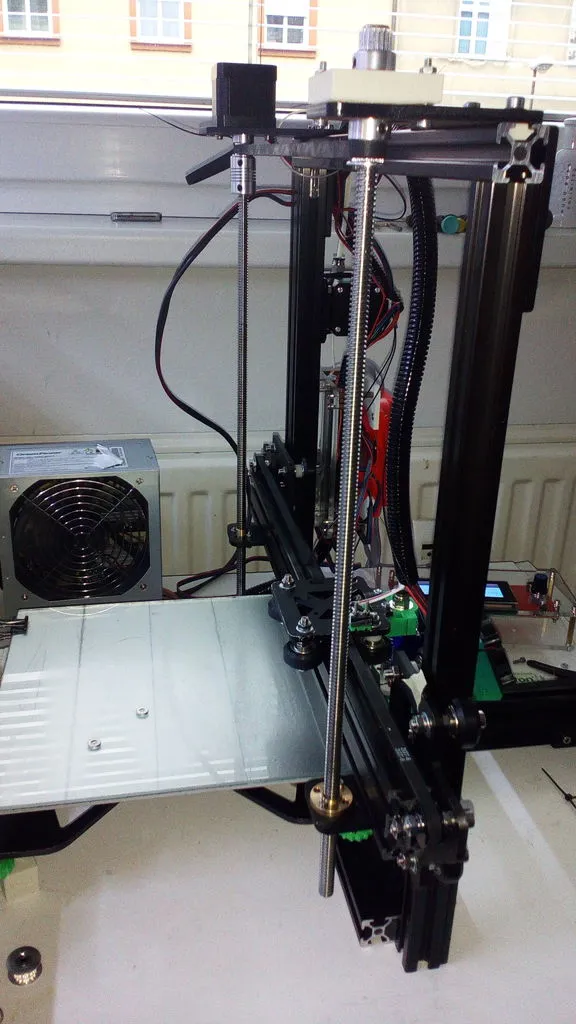
The primary symptom of loose couplers is inconsistent layer heights. You might notice that the layers are not uniform, and the print may appear wavy or uneven. This can make the object appear distorted or unstable. Another symptom is layer shifting, where the layers of the print are offset from each other. This can cause significant print failures and make the object unusable. You might also hear unusual noises, like clicking or grinding sounds, coming from the Z-axis. These sounds indicate that the coupler is slipping and not properly transferring the motor’s motion to the lead screw. If the Z-axis seems to be moving erratically or not at all, loose couplers could be the culprit. These signs should prompt an inspection of the couplers and their connections. Addressing the issue promptly can prevent more significant printing problems.
Tightening the Couplers
Tightening the couplers involves a few simple steps. First, locate the set screws on the coupler that secure it to the stepper motor shaft and the Z-axis lead screw. Use an Allen wrench or screwdriver to tighten these set screws. Ensure that the screws are firmly tightened against the shaft and the lead screw to prevent slippage. Be careful not to overtighten the screws, as this could damage the coupler or the motor shaft. After tightening the screws, manually move the Z-axis up and down to confirm the connection is secure. If the coupler still slips or if the symptoms persist, consider replacing the coupler with a new one. Many users upgrade to flexible couplers to provide some give and prevent issues like binding. Regular checks and tightening of the couplers are essential for consistent print quality and reliable Z-axis operation. This quick fix can prevent more complicated issues, so it is important to monitor and maintain. A simple Allen wrench is all you need for this.
Warped Bed
A warped bed can cause severe Z-axis problems. If the print bed is not flat, the nozzle will not maintain a consistent distance from the bed surface, leading to print adhesion problems, inconsistent first layers, and overall print failures. Warping can be caused by various factors, including uneven heating, poor bed material quality, or improper leveling. The impact of a warped bed is most noticeable during the first layer, where the nozzle’s distance from the bed must be perfect. This impacts the printer’s ability to properly lay down the first layer, which is the foundation for the entire print. Addressing bed warping is crucial for achieving successful prints. Bed flatness is a fundamental requirement for quality 3D printing, and maintaining it is a key part of overall printer maintenance. This makes bed issues one of the most critical problems to address.
Detecting Bed Warping

Detecting bed warping can be done using several methods. The simplest is to use a straight edge, such as a ruler or a metal edge, and hold it across the bed surface. Look for gaps between the straight edge and the bed. You can also use a level to check the bed’s flatness. Place the level on different areas of the bed and observe any variations. Another method is to print a large, flat object and examine the bottom layer. If the bed is warped, you may notice unevenness in the first layer. Use a feeler gauge, which is a set of thin metal blades of varying thicknesses, to measure the gap between the nozzle and the bed at different points. A significant variation in these measurements indicates warping. Modern printers often have auto-bed leveling systems, but these can only compensate for minor imperfections. Regular checks and adjustments are crucial for maintaining a flat print surface. A warped bed can significantly affect the quality of your prints.
Leveling the Bed
Leveling the bed is an essential part of ensuring good print quality. The leveling process involves adjusting the height of the bed at several points to make it as flat as possible. Many Tevo Tarantula printers use manual bed leveling, which requires you to adjust the leveling screws under the bed until the nozzle is at the correct distance from the bed in all areas. Start by heating the bed to the temperature you typically use for printing. Use a piece of paper between the nozzle and the bed to find the proper distance, adjusting the leveling screws until you feel slight resistance. Then move the nozzle around the bed and repeat the process at each corner. If your printer is equipped with an auto-bed leveling system, follow the manufacturer’s instructions to calibrate the system. After leveling, perform a test print of a small, flat object, such as a square or a calibration cube, to verify that the bed is properly leveled. If the first layer looks uneven, adjust the bed leveling again. Regularly leveling the bed is essential for achieving consistent and reliable 3D prints and ensuring that the Z-axis functions correctly.
Stepper Motor Issues
Stepper motor issues can also cause Z-axis problems. The stepper motor is responsible for controlling the movement of the Z-axis. If the motor is not functioning correctly, the Z-axis may not move smoothly or at all, leading to print failures. This can include a variety of problems, from motor failure to incorrect settings in the printer’s firmware. The stepper motor is a critical component in the 3D printing process. Without proper functioning, the Z-axis will not function and prints will be unusable. Motor issues can be complex and often require troubleshooting of the printer’s hardware and software. This may require some understanding of 3D printer electronics. This problem can be linked to many other issues, from poor power supply to worn-out drivers.
Identifying Stepper Motor Problems
Identifying stepper motor problems involves several diagnostic steps. If the Z-axis does not move, the first thing to check is whether the motor is receiving power. You can do this by checking the connections to the motor and verifying that the power supply is working. Listen for any unusual sounds coming from the motor, such as clicking or grinding noises, which may indicate a mechanical issue. Inspect the motor for any visible signs of damage, such as overheating or frayed wires. Test the motor by manually controlling it through the printer’s control panel or slicing software. If the motor makes noises but does not move, there could be a problem with the motor itself, the driver, or the wiring. Check the driver settings in your printer’s firmware to ensure the current and microstepping settings are correct for the motor. If the Z-axis frequently skips steps, the motor may not be receiving enough current or the acceleration settings may be too high. Proper identification is key to resolving stepper motor issues, minimizing print failures, and improving overall print quality.
Troubleshooting Stepper Motors
Troubleshooting stepper motors involves several steps. Check the motor connections and make sure they are secure. Ensure that the power supply is providing adequate voltage and current to the motor. Verify the wiring to eliminate any shorts or broken wires. If the motor is making noises but not moving, try adjusting the current or the microstepping settings in the firmware. If the motor is skipping steps, reduce the acceleration settings in your slicing software. If the motor is overheating, consider adding a heatsink or replacing the driver. You can also try swapping the Z-axis motor with another motor (such as the X or Y axis) to see if the problem follows the motor. If the motor is faulty, it may need to be replaced. Finally, ensure the motor is properly cooled, especially during long prints. Proper diagnosis and troubleshooting can help you resolve stepper motor issues and ensure smooth and reliable 3D printing performance. Understanding how to fix this is an important part of 3D printing.
Conclusion
Addressing these top 5 problems associated with the Tevo Tarantula Z-axis mount – Z-axis binding, misaligned Z-axis rods, loose couplers, warped beds, and stepper motor issues – can greatly improve your 3D printing experience. Regular maintenance, proper calibration, and a proactive approach to troubleshooting can keep your printer running smoothly and produce high-quality prints. By understanding these common issues and implementing the recommended solutions, you can minimize downtime and optimize the performance of your Tevo Tarantula 3D printer. Remember to regularly check and maintain your printer’s components to prevent problems from arising and to quickly address any issues that may occur. With a little effort, you can keep your Tevo Tarantula in top condition and consistently achieve excellent 3D printing results. The key is proactive maintenance.
